Homeownership is a significant milestone and a cherished dream for many Americans. It represents stability, security, and a place to create lasting memories. However, with homeownership comes the responsibility of safeguarding this valuable asset from unexpected events that could jeopardize it.
Mortgage protection with life insurance shields your investment in your dream home against financial risks posed by the unexpected. But should you choose Mortgage Protection Insurance (MPI)? Or is there an alternative?
In this blog, we’ll explore the different aspects of mortgage protection insurance, how it can provide you peace of mind, and if it’s the right option for your situation.
What is Mortgage Protection Insurance?
Mortgage Protection Insurance (MPI) is a specialized form of insurance designed to safeguard homeowners against unexpected events that could impact their ability to meet mortgage payments. MPI provides financial protection by stepping in to cover mortgage expenses or paying off the mortgage balance in case of qualifying events such as death, disability, or critical illness.
Unlike homeowners insurance, which primarily focuses on property damage and liabilities, MPI centers around the financial aspect of homeownership. It acts as a safety net, ensuring your mortgage obligations are met during challenging times, reducing the risk of foreclosure or financial distress for you and your loved ones.
Traditional insurance companies don’t offer this service. Speak with your mortgage lender or contact your local bank if you’re interested in buying a mortgage protection policy.

Types of Mortgage Protection
Differences Between Mortgage Protection Insurance (MPI), Private Mortgage Insurance (PMI), and Mortgage Insurance Premiums (MIP)
Mortgage protection insurance isn’t the only kind of mortgage coverage out there. Here are two other types: private mortgage insurance and mortgage insurance premiums.
Mortgage Protection Insurance (MPI) vs. Private Mortgage Insurance (PMI)
Mortgage protection and private mortgage insurance are two distinct coverage types with the same basic principle of offering financial protection. But who benefits from either is different, and it is crucial for you, as a homeowner, to understand these defining differences and similarities.
Your option depends on the required coverage and your specific needs and circumstances.
1 | Purpose and Coverage Focus
The main difference between them lies in their purpose and coverage focus.
Mortgage Protection Insurance: Mortgage protection insurance provides financial security for homeowners and their families in unexpected circumstances like death, disability, or critical illness.
It targets mortgage obligations, aiming to pay off or cover the outstanding mortgage balance in the event of the policyholder’s death or provide temporary assistance with mortgage payments during disability or critical illness.
This coverage protects your home from foreclosure as it clears your mortgage balance.
Private Mortgage Insurance: Private mortgage insurance, commonly known as PMI, protects lenders against the risk of default by borrowers with a down payment of less than 20% when purchasing a home.
PMI focuses on protecting the lender’s investment in the property, providing reimbursement to the lender if the borrower defaults on the mortgage. It does not cover any outstanding balances, prevent your home from going into foreclosure or safeguard your family’s living conditions.
2 | Beneficiary
In both instances, the lender is the primary beneficiary of mortgage protection and private mortgage insurance. Your lender will receive the entirety of the payout as compensation to recoup their investment.
3 | Payment Responsibility
Mortgage Protection Insurance: The homeowner is responsible for paying the premiums for mortgage protection insurance.
Private Mortgage Insurance: There are four main repayment options:
- Lender-paid: the insurance is part of the loan, and you can’t cancel it without refinancing
- Borrower-paid: the most common form that comes as an additional monthly fee added to your mortgage payment
- Single-premium: payment of the insurance in one upfront lump sum
- Split-premium mortgage insurance: it’s a hybrid of borrower-paid and single premium with a partial upfront payment with the balance covered as monthly payments
4 | Duration of Coverage
Mortgage Protection Insurance: The coverage duration for mortgage protection insurance extends for the life of your mortgage. It’s a term policy with a reduced payout balance tied to your mortgage’s outstanding funds.
Private Mortgage Insurance: borrower-paid PMI is not a permanent fixture on your mortgage. You can remove it once your loan-to-value (LTV) ratio reaches 80%, meaning you’ve repaid 20% of the home’s value through equity or appreciation.

Mortgage Protection Insurance (MPI) vs. Mortgage Insurance Premium (MIP)
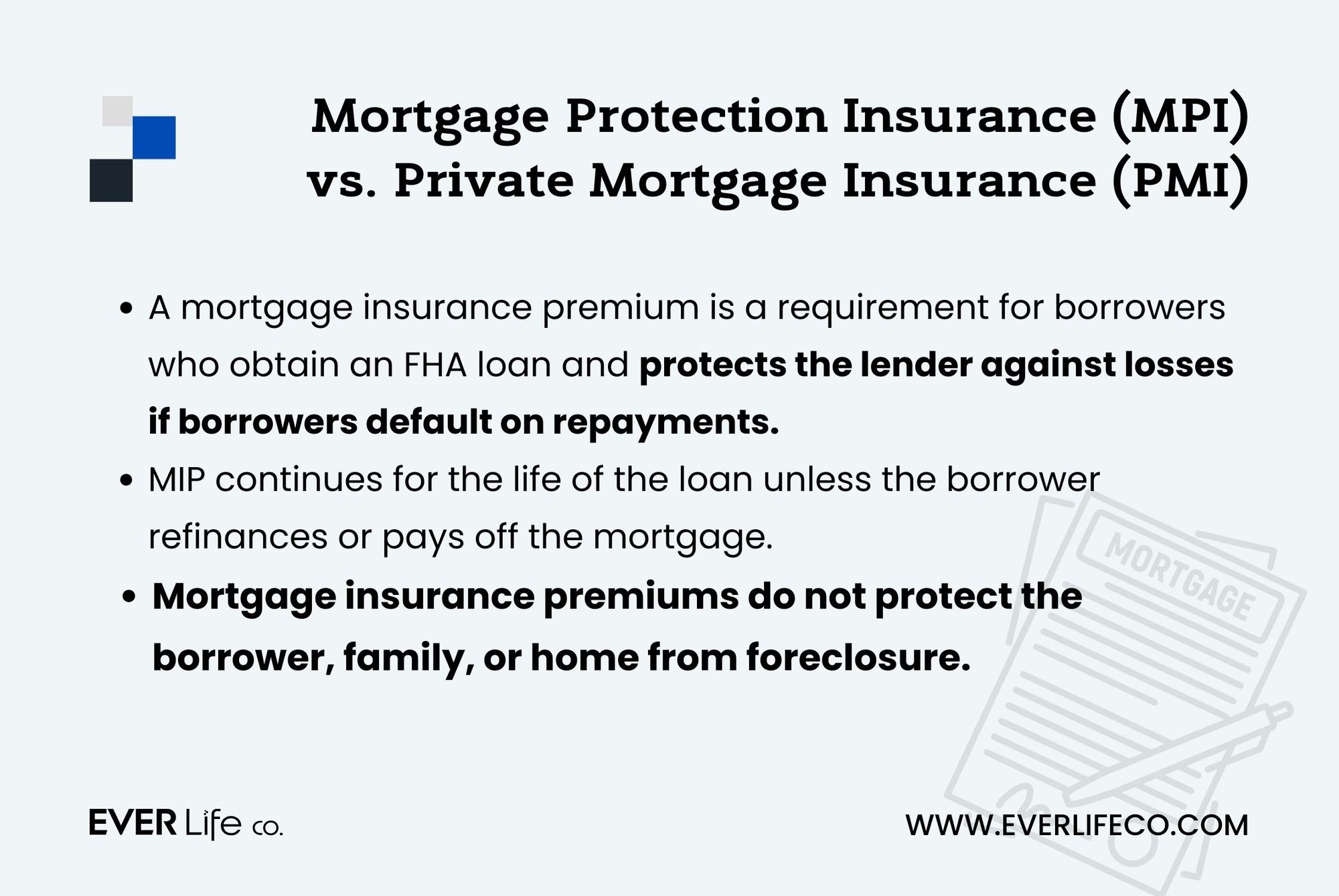
MPI also differs from the mortgage insurance premium (MIP) attached to a Federal Housing Administration (FHA) loan. FHA’s mortgage insurance premium is a requirement for borrowers who obtain an FHA loan, a government-backed loan scheme for potential homebuyers.
As with private mortgage insurance, MIP protects the lender against losses if borrowers default on repayments by reimbursing the outstanding balance. The mortgage lender is the sole beneficiary.
This insurance continues for the life of the loan unless the borrower refinances into a conventional loan or pays off the mortgage entirely. And like PMI, mortgage insurance premium doesn’t protect you, your family, or your home from foreclosure.
Pros and Cons of Mortgage Protection Insurance
Mortgage protection insurance is a primary recommendation for individuals who encounter challenges obtaining conventional/traditional life or disability insurance or find the monthly payments for such policies costly.
If you find yourself in this particular circumstance, weigh the advantages and disadvantages of mortgage protection insurance and how it can benefit you in the long run.
The Benefits of Mortgage Protection
Simplified Underwriting
MPI offers coverage with simplified underwriting, meaning you may not require extensive medical examinations or complex paperwork to obtain coverage. This streamlined approach makes MPI accessible and convenient, allowing you to secure protection quickly and efficiently.
Simplified underwriting is advantageous to applicants with severe health issues who face hiked rates for traditional coverage or struggle to obtain a policy because of the risk they pose to an insurance company.
Financial Security
One of the primary benefits of Mortgage Protection (MPI) is the assurance of financial security it provides. Life is unpredictable, and unfortunate events such as disability, illness, or even untimely death can significantly impact your ability to make mortgage payments.
MPI is a safety net, covering your mortgage obligation during difficult times or paying it off altogether. This protection allows you and your loved ones to remain in your home without the added burden of worrying about mortgage payments, providing stability and preserving the sanctuary you’ve worked hard to create.
But despite its advantages, MPI has its drawbacks.
The Downside of Mortgage Protection Insurance
Limited Coverage Scope
One of the main disadvantages of mortgage protection insurance is that it provides coverage only for mortgage-related obligations. While it repays mortgage amounts in the event of death, disability, or critical illness, it does not cover other financial responsibilities such as household bills, living expenses, or other debts.
Limited Flexibility and Portability
Mortgage protection insurance is typically tied to a specific mortgage loan. If the homeowner decides to refinance the mortgage or move to a new home, the existing policy may not be transferable, or your lender might require adjustments.
This lack of flexibility and portability is a disadvantage, as you may need to secure new coverage or navigate the complexities of transferring the policy to the new mortgage.
Premium Costs
The premiums associated with mortgage protection insurance (MPI) frequently exceed those of traditional term life insurance. This disparity arises because term life insurance typically involves comprehensive medical underwriting, wherein your health condition is pivotal in rate determination.
While purchasing a term life policy requires a medical examination, the advantage lies in the insurer’s ability to assess your health accurately, enabling them to offer more competitive rates.
Your good health is a significant advantage you should use whenever possible. This is why mortgage protection insurance isn’t the best choice for all homeowners since there is probably a better alternative.
Better Alternatives Exist
Exploring potential alternatives is crucial as mortgage protection insurance (MPI) solely serves to settle your mortgage balance in the event of your demise, offering limited financial protection to your loved ones.
Opting for a life insurance policy may prove more sensible as you choose your beneficiaries, granting them the autonomy to allocate the funds according to their needs, whether towards the mortgage or other purposes.

Traditional Life Insurance vs. Mortgage Protection Plan
Several key factors come into play when considering the advantages of traditional life insurance over mortgage protection insurance policies.
Comprehensive Financial Protection
Traditional life insurance offers broader financial protection to your loved ones beyond only paying off mortgage debt. Beneficiaries can utilize the policy’s death benefit for various purposes, such as funeral expenses, replacing lost income, covering daily expenses, funding education, or paying off debts other than the mortgage.
Flexibility in Fund Allocation
Like MPI, traditional policies provide a death benefit payout in the event of your passing. However, the difference is that the death benefit is not limited to mortgage repayment. Your beneficiaries can choose how to best utilize the funds based on their circumstances and financial priorities.
This flexibility enables them to address immediate financial needs or allocate funds for long-term financial security.
Lower Premiums for Healthy Individuals
Life insurance premiums, particularly for non-smokers in good health, are generally lower than MPI. Traditional life insurance policies often involve more thorough underwriting, considering various aspects such as medical history, lifestyle, and family health.
By undergoing full medical underwriting during the application process, insurance providers can assess your health accurately and offer competitive rates based on the lower risk you pose.
On top of that, term policies are cheaper than permanent policies as they don’t carry a cash value, and they’re temporary—unless you decide to upgrade to a permanent policy at the end of the initial term.
Portability and Coverage Duration
Traditional life insurance policies are typically portable, meaning you can maintain coverage even if you switch lenders or move to a new home. Moreover, term life insurance policies can be purchased for specific durations (e.g., 10, 20, or 30 years), providing coverage that aligns with your mortgage term or desired protection period.
Potential Cash Value Accumulation
Certain types of life insurance, such as whole life or universal life coverage, offer the potential for cash value accumulation over time. These policies deliver both protection and a savings component, allowing you to access accumulated cash value during your lifetime or transfer wealth to your beneficiaries as an estate planning tool.
Additional Insurance Protection
You can purchase optional riders for extra protection with permanent life insurance or a traditional term policy.
For example, a critical illness rider pays a lump-sum benefit if you’re diagnosed with a specified critical illness.

Learn more about life insurance riders and how they act as an extra layer of financial protection for you and your family.
Choosing Between Traditional Term Life Insurance and Mortgage Protection Life Insurance
The closest alternative to mortgage protection insurance is a term life policy. Choosing which to purchase depends on your circumstances and financial goals.
Consider the following factors:
- Coverage Needs: Assess your overall financial obligations and goals beyond mortgage repayment. If you want comprehensive protection that extends to your beneficiaries’ income replacement, education expenses, and other financial needs, a term life insurance policy is better. On the other hand, if your primary concern is ensuring the mortgage is paid off in the event of your passing, MPI may be more suitable.
- Cost Considerations: Compare the premiums of term life insurance and MPI. Term life insurance premiums are often lower, especially for healthy and non-smoking individuals. If the cost of MPI is significantly higher, and you can obtain sufficient coverage with term life insurance, it’s a more cost-effective option.
- Flexibility and Portability: Term life insurance policies are flexible and portable. They can cover various financial needs beyond the mortgage, and you can maintain coverage even if you switch lenders or move to a new property. If you value the flexibility to allocate funds based on your beneficiaries’ needs and want coverage that adapts to changes in your circumstances, term life insurance is preferable.
- Underwriting Requirements: MPI often involves limited or no medical underwriting, making it accessible to individuals with difficulty obtaining traditional life coverage due to health conditions. If health concerns impact your ability to secure term life insurance, MPI may be a more viable option.
- Duration of Coverage: Consider the term length of the coverage you require. If it aligns closely with your mortgage term, MPI may be a convenient choice as it specifically addresses the mortgage obligation during that period. However, if you desire coverage beyond the mortgage term to provide ongoing financial security for your loved ones, term life insurance offers a more suitable solution.
Conclusion
Mortgage protection with life insurance offers a valuable layer of security for your home and loved ones. You can obtain a mortgage protection policy from your lender or choose a standard term life policy from an insurance company.
Whichever option you select depends on your financial situation.
Don’t leave the protection of your dream home to chance. Take action today to protect what matters and enjoy the peace of mind of knowing you’ve secured your investment for the long haul.






